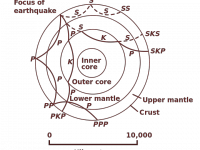
Beno Gutenberg and the Earth’s Interior
On June 4, 1889, German-American seismologist Beno Gutenberg was born. Gutenberg is noted for his analyses of earthquake waves and the information they furnish about the physical properties of the Earth’s interior. He was a colleague and mentor of Charles Francis Richter at the California Institute of Technology and Richter’s collaborator in developing the Richter magnitude scale for measuring an earthquake’s magnitude. Beno Gutenberg – Early Years Beno Gutenberg was born in…
Read more