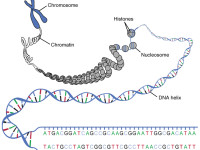
Alfred Sturtevant and the Chromosomes
On November 21, 1891, American geneticist Alfred Henry Sturtevant was born. Sturtevant constructed the first genetic map of a chromosome in 1913. Throughout his career he worked on the organism Drosophila melanogaster with Thomas Hunt Morgan. By watching the development of flies in which the earliest cell division produced two different genomes, he measured the embryonic distance between organs in a unit which is called the sturt in his honor. Alfred Sturtevant…
Read more