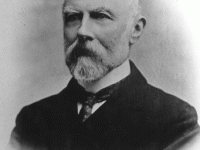John Herschel – a Pioneer in Celestial Photography
On March 7, 1792, English polymath, mathematician, astronomer, chemist, inventor, and experimental photographer Sir John Herschel was born. Herschel originated the use of the Julian day system in astronomy and named seven moons of Saturn and four moons of Uranus. He made many contributions to the science of photography, and investigated colour blindness and the chemical power of ultraviolet rays. Overall, he advocated an inductive approach to scientific experiment and theory building,…
Read more