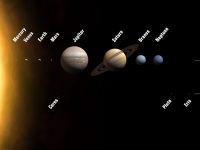
To be or Not to be a Planet – Eris, the planet of Discord
On October 21, 2003, a photograph of the nocturnal sky was taken, where almost 2 years later, in January 2005, evidence was raised that there might be a 10th planet at the borders of our solar system: Eris, located in the Kuiper Belt and named after the Greek goddess of discord. And discord it should be, because Eris as a planet is rather small and astronomers were arguing, whether it is a…
Read more