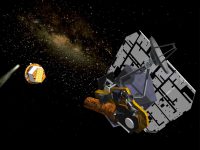
Deep Impact and the Comet 9P/Tempel
On January 12, 2005, NASA space probe Deep Impact was launched. It was designed to study the interior composition of the comet 9P/Tempel, by releasing an impactor into the comet, which successfully collided with the comet’s nucleus. Deep Impact – Mission Background The main mission of Deep Impact was to explore the interior of Temple 1 by placing a 372 kg heavy projectile (impactor) into the trajectory of the comet, which hit it…
Read more