Alec Jeffreys and the Genetic Fingerprint
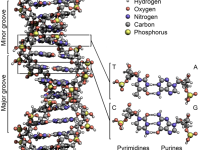
On January 9, 1950, British geneticist Alec Jeffreys was born. In 1984, Jeffreys developed techniques for DNA fingerprinting and DNA profiling which are now used worldwide in forensic science to assist police detective work and to resolve paternity and immigration disputes. Alec Jeffries – Youth and Education Alec John Jeffreys was born into a middle-class family in Oxford, UK, where he spent the first six years of his life until 1956, when the family moved to Luton,…
Read more