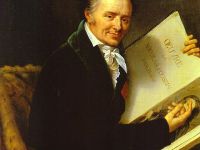The Comte de Caylus and the Birth of Archaeology
On September 5, 1765, French antiquarian, proto-archaeologist and man of letters Anne Claude de Tubières-Grimoard de Pestels de Lévis, comte de Caylus, marquis d’Esternay, baron de Bransac, was born. The Comte de Caylus is credited with being the first to conceive archaeology as a scientific discipline. Caylus was also a painter and an engraver, and he is also credited with finding a new process to inlay colors in marble. The Comte de…
Read more