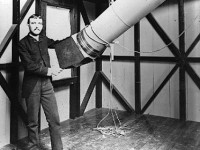
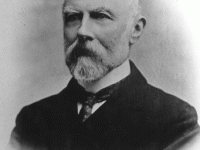Henry Draper and his Passion for Astronomy
On March 7, 1837, American physiologist and amateur astronomer Henry Draper was born. He is best known today as a pioneer of astrophotography. After his death, the Henry Draper Catalog of stellar spectra as well the Henry Draper medal is named after him. Henry Draper – Early Years Henry Draper was the son of John William Draper,[6] a doctor, chemist, and professor at New York University. He was known for his interest in…
Read more