Maurice Wilkins and the Riddle of the DNA Structure
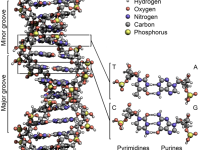
On December 15, 1916, New Zealand-born British physicist, molecular biologist, and Nobel Laureate Maurice Wilkins was born. Wilkins’ research contributed to the scientific understanding of phosphorescence, isotope separation, optical microscopy and X-ray diffraction, and to the development of radar. He is best known for his work at King’s College London on the structure of DNA. “It is essential for genetic material to be able to make exact copies of itself; otherwise growth…
Read more