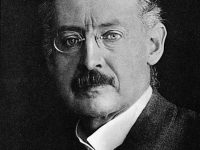Jacques Hadamard and the Description of Mathematical Thought
On December 8, 1865, French mathematician Jacques Salomon Hadamard was born. Hadamard made major contributions in number theory, complex function theory, differential geometry and partial differential equations. Moreover, he is also known for his description of the mathematical though process in his book Psychology of Invention in the Mathematical Field. “It is important for him who wants to discover not to confine himself to one chapter of science, but to keep in…
Read more